Embark on a celestial journey with How to Use Stargazing Apps on Your Smartphone! Imagine holding the universe in your hand, ready to explore constellations, planets, and nebulae with just a few taps. This guide is your personal passport to the cosmos, transforming your smartphone into a powerful stargazing tool. From the basics to advanced features, we’ll navigate the night sky together, making astronomy accessible and fun for everyone.
We’ll delve into the exciting world of stargazing apps, exploring how they work and how they’ve revolutionized the way we observe the stars. We’ll cover everything from choosing the right app and downloading it, to using its features to identify celestial objects and plan your stargazing sessions. Whether you’re a curious beginner or a seasoned stargazer, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to unlock the wonders of the night sky.
Introduction to Stargazing Apps
Stargazing apps have revolutionized how we explore the night sky, transforming what was once a pastime requiring extensive knowledge and specialized equipment into an accessible and engaging experience for everyone. These apps bring the wonders of the cosmos to your fingertips, providing real-time information about celestial objects and guiding you on your astronomical journey. They bridge the gap between curiosity and understanding, making stargazing more approachable and enjoyable than ever before.
Basic Concept and Purpose
Stargazing apps are essentially pocket-sized planetariums. They use your smartphone’s sensors, such as the GPS, compass, and accelerometer, to determine your location and orientation. This information is then used to display a real-time, interactive map of the night sky, showing you the positions of stars, planets, constellations, and other celestial objects visible from your current location. The primary purpose of these apps is to educate and entertain, making it easier for users to identify objects in the night sky, learn about astronomy, and plan their stargazing sessions.
Brief History of Stargazing and Technological Impact
Stargazing has a rich history, dating back to ancient civilizations who used the stars for navigation, agriculture, and religious purposes. Early stargazers relied on their observations, memory, and simple tools like astrolabes and armillary spheres to understand the cosmos. The invention of the telescope in the early 17th century marked a turning point, enabling astronomers to observe celestial objects in greater detail.The advent of technology, particularly the personal computer and the internet, further transformed astronomy.
Software programs provided detailed star charts and simulated celestial events. However, the real game-changer was the smartphone. With the integration of sensors and powerful processing capabilities, smartphones enabled the creation of user-friendly stargazing apps that could be used anywhere, anytime. This shift democratized astronomy, making it accessible to anyone with a smartphone.
Benefits for Beginners and Experienced Stargazers
Stargazing apps offer numerous benefits, catering to both beginners and experienced stargazers.For beginners:
- Easy Identification: Apps can instantly identify stars, planets, and constellations simply by pointing your phone at the sky.
- Educational Resources: Many apps include detailed information about celestial objects, constellations, and astronomical events.
- Guided Tours: Some apps offer guided tours of the night sky, leading you to specific objects and providing context.
- Planning Tools: Apps help you plan stargazing sessions by showing you when and where celestial objects will be visible.
For experienced stargazers:
- Quick Reference: Apps serve as a quick reference tool for identifying objects and confirming observations.
- Advanced Features: Many apps offer advanced features, such as augmented reality views, telescope control, and data on deep-sky objects.
- Real-Time Information: Apps provide up-to-date information on celestial events, such as meteor showers and planetary alignments.
- Planning Assistance: They assist in planning observing sessions, identifying the best times to view specific objects based on light pollution and weather conditions.
Choosing the Right Stargazing App

Selecting the ideal stargazing app is crucial for maximizing your astronomical adventures. With a plethora of options available, understanding the key features and comparing different apps will help you find the perfect celestial companion for your smartphone. This section will guide you through the essential elements to consider when making your choice.
Key Features to Look For in a Stargazing App
A good stargazing app should offer a comprehensive set of features to enhance your experience. These features cater to both novice and experienced stargazers, making the night sky more accessible and enjoyable.
- Real-Time Sky Mapping: This feature displays the current position of stars, planets, constellations, and other celestial objects based on your device’s location and time. It’s the foundation of any effective stargazing app.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Mode: AR mode overlays information about celestial objects onto your phone’s camera view, allowing you to identify objects simply by pointing your phone at the sky.
- Extensive Database: The app should include a vast database of celestial objects, including stars, planets, constellations, galaxies, nebulae, and even artificial satellites like the International Space Station (ISS).
- User-Friendly Interface: The app’s interface should be intuitive and easy to navigate, even in low-light conditions.
- Search Functionality: A search function enables you to quickly locate specific objects by name or type.
- Offline Functionality: The ability to download data and use the app offline is essential, especially when stargazing in remote locations without internet access.
- Constellation Information: Detailed information about constellations, including their history, mythology, and notable stars.
- Light Pollution Filter: Some apps include a light pollution filter to simulate how the night sky would appear from a darker location.
- Time Controls: Time controls allow you to simulate the night sky at different times, both past and future, to observe celestial events.
- Notifications: Notifications for upcoming astronomical events, such as meteor showers, planetary alignments, and eclipses.
Comparing Popular Stargazing Apps
Several excellent stargazing apps are available, each with its strengths and weaknesses. This comparison provides an overview of some of the most popular options.
| App Name | Key Features | User Rating |
|---|---|---|
| SkyView Lite | AR mode, object identification, extensive database, social sharing, light pollution filter | 4.6 stars (based on user reviews) |
| Star Walk 2 | AR mode, time machine, night mode, detailed information on celestial objects, notifications, and Apple Watch support | 4.7 stars (based on user reviews) |
| Stellarium Mobile | Realistic sky simulation, detailed object information, time controls, offline use, and a wide array of settings. | 4.5 stars (based on user reviews) |
| SkySafari | Vast database, telescope control, advanced simulations, deep-sky object information, and light pollution filter | 4.8 stars (based on user reviews) |
Note: User ratings can vary depending on the platform and the source of the review. These ratings are approximate and intended for comparison purposes.
Different App Types and Their Suitability for Various Users
Stargazing apps come in different types, each designed with specific user needs in mind. Understanding the distinctions between these app types can help you choose the one that best fits your experience level and interests.
- Basic Sky Maps: These apps provide a fundamental view of the night sky, displaying stars, planets, and constellations in real-time. They are excellent for beginners who are new to stargazing. An example is SkyView Lite.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Apps: AR apps use your phone’s camera to overlay information about celestial objects onto the real-world view of the sky. This type is user-friendly for identifying objects in the sky. Star Walk 2 is a prime example of this app type.
- Advanced Sky Simulators: These apps offer a more comprehensive experience, including detailed information on celestial objects, telescope control, and advanced simulations. SkySafari is an example of this type, suitable for experienced stargazers.
- Educational Apps: Some apps focus on providing educational content about astronomy, including information on constellations, mythology, and the history of space exploration.
Downloading and Installing Stargazing Apps

Now that you’ve chosen the perfect stargazing app for your needs, it’s time to get it onto your smartphone. This section will guide you through the download and installation process for both iOS and Android devices, along with some helpful troubleshooting tips to get you up and running quickly. We’ll also cover app updates and permission management.
Downloading Stargazing Apps on iOS
Downloading and installing apps on iOS devices, like iPhones and iPads, is a straightforward process facilitated by the App Store.To download a stargazing app on iOS:
- Open the App Store: Locate and tap the App Store icon on your home screen. It’s a blue icon with a white “A” inside.
- Search for the App: Tap the search icon (usually a magnifying glass) at the bottom of the screen. In the search bar, type the name of the stargazing app you want to download (e.g., “SkyView Lite,” “Star Walk 2,” or the name of the app you chose previously).
- Select the App: From the search results, tap on the app you’re looking for. Make sure it’s the correct app by checking the developer and app description.
- Download the App: Tap the “Get” button (or the cloud icon with a downward-pointing arrow if you’ve downloaded it before). You may be prompted to enter your Apple ID password or use Face ID/Touch ID to authenticate the download.
- Wait for Installation: The app will begin downloading and installing. You’ll see a progress bar indicating the download’s progress. Once the download is complete, the “Get” button will change to “Open.”
- Open the App: Tap the “Open” button to launch the stargazing app. You might be asked to grant permissions (e.g., access to your location, camera).
Downloading Stargazing Apps on Android
The process for downloading and installing stargazing apps on Android devices is similar to iOS, but uses the Google Play Store.To download a stargazing app on Android:
- Open the Google Play Store: Find the Google Play Store app on your home screen or app drawer. It’s a colorful icon that looks like a play button.
- Search for the App: Tap the search bar at the top of the screen and type the name of the stargazing app you want to download.
- Select the App: From the search results, tap on the app you wish to download. Verify the app by checking the developer and app description.
- Install the App: Tap the “Install” button. You might be prompted to grant permissions required by the app.
- Wait for Installation: The app will download and install automatically. A progress bar will show the download’s progress. Once finished, the “Install” button will change to “Open.”
- Open the App: Tap the “Open” button to launch the stargazing app. You may be asked to grant permissions.
Troubleshooting Common Installation Issues
Sometimes, the installation process doesn’t go smoothly. Here are some common issues and how to resolve them:
- Insufficient Storage Space: Ensure your device has enough free storage space. Apps can require significant storage. If your device is full, delete unnecessary files, photos, videos, or other apps. You can check storage usage in your device’s settings (e.g., Settings > General > iPhone Storage on iOS, or Settings > Storage on Android).
- Poor Internet Connection: A stable internet connection is essential for downloading apps. If the download is slow or fails, try connecting to a Wi-Fi network or moving to an area with better cellular service.
- App Compatibility: Make sure the app is compatible with your device’s operating system version. Check the app’s description in the App Store or Google Play Store for compatibility requirements. If your device is running an outdated operating system, consider updating it (Settings > General > Software Update on iOS, or Settings > About Phone > Software Information > Android).
- App Download Issues: Sometimes, the app store itself might experience temporary glitches. Try restarting your device, clearing the cache of the App Store or Google Play Store (in Settings > Apps > [App Store/Google Play Store] > Storage > Clear Cache), or checking the app store’s status online.
- Authentication Problems: If you are having trouble authenticating (e.g., entering the correct password), verify your Apple ID or Google account details. Make sure you are using the correct password and that your account is active.
Updating Apps and Managing App Permissions
Keeping your stargazing apps updated and managing their permissions is crucial for optimal performance and security.
Updating Apps:
Regularly updating your stargazing apps ensures you have the latest features, bug fixes, and performance improvements.
Here’s how to update apps on iOS and Android:
- iOS:
- Open the App Store.
- Tap on your profile icon in the top-right corner.
- Scroll down to see a list of apps with available updates.
- Tap “Update” next to individual apps, or tap “Update All” to update all apps.
- Android:
- Open the Google Play Store.
- Tap on your profile icon in the top-right corner.
- Tap “Manage apps & device.”
- Under “Updates available,” tap “See details.”
- Tap “Update” next to individual apps, or tap “Update all.”
Managing App Permissions:
App permissions control what features of your device an app can access. Managing these permissions is vital for your privacy and security.
Here’s how to manage app permissions:
- iOS:
- Go to Settings > Privacy.
- Tap on the permission you want to manage (e.g., Location Services, Camera, Microphone).
- You’ll see a list of apps that have requested access to that permission.
- Toggle the switch to grant or deny access to each app. You can also select “While Using the App” for location services to grant access only when the app is in use.
- Android:
- Go to Settings > Apps.
- Tap on the stargazing app you want to manage.
- Tap “Permissions.”
- You’ll see a list of permissions the app requests (e.g., Location, Camera, Contacts).
- Toggle the switches to grant or deny access to each permission.
Navigating the App Interface

Now that you’ve chosen and installed your stargazing app, it’s time to explore its interface. Understanding the layout and controls is key to unlocking the app’s full potential and enjoying your stargazing experience. Most stargazing apps share common elements, but the specific design can vary.
Core Components of a Typical Stargazing App Interface
Most stargazing apps present a similar core interface designed to provide a user-friendly experience. This typically includes a main view displaying the current sky, overlaid with information about celestial objects.* Main Sky View: This is the primary display, showing the stars, planets, constellations, and other celestial objects visible from your location. The app uses your device’s sensors to determine the direction you’re pointing it, updating the view in real-time.
The main view’s appearance is influenced by the time of day, location, and date, simulating the night sky accurately.
Information Overlays
Overlays provide supplementary data about the objects displayed in the main view. This might include the names of stars and constellations, planetary positions, and information on deep-sky objects like nebulae and galaxies. These overlays can usually be toggled on or off to declutter the view.
Control Panel/Menu
This area houses the app’s controls, allowing you to adjust settings, access information, and perform searches. Common features include a search function, a settings menu for location and display preferences, and options to control the display of information overlays.
Time Controls
Time controls are an essential component, enabling you to simulate the sky at different times. You can fast-forward or rewind time to observe the movement of celestial objects over hours, days, or even years. This feature helps you predict the visibility of objects and plan your stargazing sessions.
Compass/Orientation Indicators
Many apps incorporate a compass or orientation indicator to help you understand the direction your device is pointing. This is especially useful if you are unfamiliar with the night sky and need help identifying constellations or locating specific objects.
Using the Search Function to Locate Celestial Objects
The search function is an indispensable tool for any stargazing app, allowing you to quickly locate specific objects in the sky. This feature typically works by typing in the name of the object you want to find, such as a planet, star, constellation, or deep-sky object.* Entering the Object’s Name: Begin by tapping on the search icon, usually represented by a magnifying glass.
Then, type the name of the celestial object you are interested in. For example, if you want to find the planet Jupiter, type “Jupiter” into the search bar. The app will typically offer suggestions as you type, which can speed up the process.
Selecting the Object
Once you’ve typed in the object’s name, the app will display a list of matching results. Select the correct object from the list. The app will then center the main sky view on the chosen object, highlighting its position in the sky.
Using the “Go To” Feature
After selecting the object, most apps will have a “Go To” or “Locate” feature. This feature will guide you to the object by displaying an arrow or a crosshair on the screen. Follow the arrow to point your device towards the object’s location in the sky.
Accessing Object Information
Once the object is located, the app will provide detailed information. This information may include the object’s distance, magnitude (brightness), type, and other relevant data. Many apps also offer links to more in-depth information from external sources, like Wikipedia or the object’s entry in the Messier or Caldwell catalogs.
Using Alternate Names/Designations
When searching, be aware that objects may have multiple names or designations. For example, the Orion Nebula is also known as Messier 42 (M42). If you can’t find an object using one name, try another. You can often find alternate names through online astronomy resources.
User Interface Tutorial
This tutorial will guide you through the common interface elements of a stargazing app. While the specific layout might vary depending on the app, the core functionalities are typically similar. Imagine you’re looking at the screen of a typical stargazing app.* Main Sky View: This is the central area of the screen, displaying a realistic representation of the night sky.
It shows stars, planets, constellations, and other celestial objects. As you move your device, the view updates in real-time to match the sky in front of you.
Search Icon
Typically represented by a magnifying glass, tap this icon to open the search function.
Settings Menu
Usually found as a gear icon or three vertical dots, this menu allows you to customize the app’s settings. You can adjust the location, time, display preferences (e.g., constellation lines, object labels), and other features.
Time Controls
Look for forward and backward arrows or a time slider. These controls allow you to change the time, letting you observe the movement of celestial objects.
Object Information Panel
After selecting an object, this panel appears, providing details like its name, distance, magnitude, and other relevant information.
Compass Indicator
Often located at the top or bottom of the screen, this indicator helps you understand which direction your device is pointing.
Constellation Lines
These are lines that connect the stars, forming the recognizable shapes of constellations. They can usually be toggled on or off in the settings menu.
Object Labels
These labels display the names of stars, planets, and other objects. They can also be toggled on or off.
Using the App to Identify Celestial Objects
Now that you’ve got your stargazing app downloaded and ready, it’s time to put it to work! The primary function of these apps is to help you identify what you’re seeing in the night sky. This section will guide you through the process, from pointing your phone upwards to recognizing various celestial objects.
Identifying Stars, Planets, and Constellations
The core function of any stargazing app is to identify objects in the night sky. This is usually achieved using your phone’s sensors, primarily the gyroscope, compass, and GPS.Here’s how to use your app to identify celestial objects:
1. Launch the App and Enable Location Services
Open your stargazing app and ensure location services are enabled. This allows the app to know your precise location and accurately display the sky from your vantage point.
2. Point Your Phone at the Sky
Hold your phone up and point it towards the area of the sky you’re interested in. The app will use your phone’s sensors to determine its orientation.
3. Observe the Display
The app will overlay information onto your phone’s screen, identifying stars, planets, constellations, and other objects. The display will likely update in real-time as you move your phone around.
4. Tap on Objects for More Information
Tap on any identified object to learn more about it. You’ll typically find details like the object’s name, distance, magnitude (brightness), and other interesting facts.
5. Use Filters and Search
Most apps offer filters to help you focus on specific objects. You might filter by planet, constellation, or even specific deep-sky objects. You can also use the search function to locate a particular object.
Using Augmented Reality (AR) Features
Augmented reality (AR) features enhance the stargazing experience by overlaying celestial information onto the real-world view of the sky.Follow these steps to use the AR features:
1. Enable AR Mode
Look for an AR icon (often a camera icon or a symbol representing a view of the sky with overlaid information) within the app. Tap this icon to activate AR mode.
2. Point Your Phone at the Sky
The app will use your phone’s camera to display the real-time view of the sky. As you move your phone, the app will overlay information about stars, planets, and constellations directly onto the camera’s feed.
3. Adjust Brightness and Contrast (if needed)
In some situations, the AR overlay might be difficult to see. Adjust the brightness or contrast settings within the app to improve visibility. This is particularly useful in areas with light pollution.
4. Explore and Learn
Move your phone around to explore the sky. The app will identify objects in real-time, allowing you to learn about constellations, planets, and other celestial wonders.
Common Celestial Objects and Their Appearances
Knowing what to expect can greatly enhance your stargazing experience. Here’s a list of common celestial objects and their typical appearances through a stargazing app:
- Stars: Appear as small, twinkling points of light. Their colors can vary (blue, white, yellow, red), depending on their temperature. The app will show their names, distances, and sometimes their constellations.
-
Planets: Generally appear as brighter, steady points of light that don’t twinkle as much as stars. Planets move across the sky in a predictable way. The app will display their names, current positions, and orbital paths.
- Jupiter: Often appears as a bright, yellowish object. The app might show its Galilean moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto) if your phone’s screen and the app’s capabilities allow for it.
- Saturn: Easily recognizable by its yellowish hue. If the app shows a detailed enough view, you might even see its rings.
- Mars: Appears reddish. Its brightness varies depending on its proximity to Earth.
- Venus: The brightest planet, often seen near the horizon, and can appear very bright.
- Constellations: Groupings of stars that form recognizable patterns. The app will draw lines connecting the stars, making it easier to identify the constellations.
- The Moon: A large, bright object that changes phases throughout the month. The app will show the current phase of the Moon.
- Deep-Sky Objects (Nebulae, Galaxies, Star Clusters): Appear as faint, fuzzy patches of light. Some of the brighter objects, like the Orion Nebula (M42), can be seen with the naked eye under dark skies, and are easily located with the app.
Advanced Features and Settings
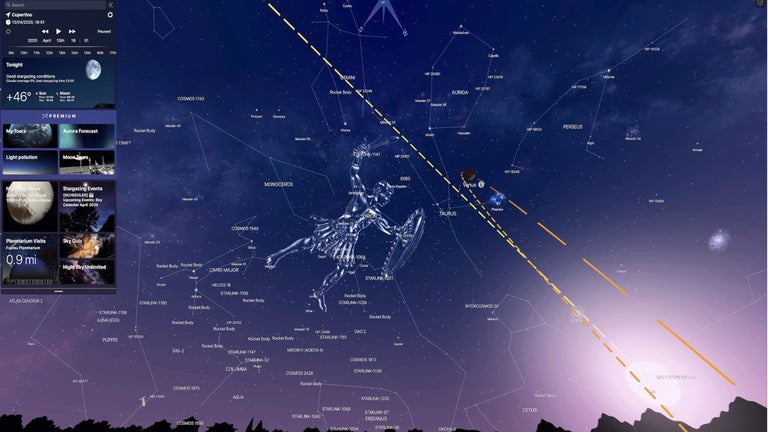
Now that you’re comfortable navigating the basic features of your stargazing app, let’s dive into the more advanced settings and tools that can significantly enhance your stargazing experience. These features allow for a more personalized and in-depth exploration of the night sky.
Customizing Location, Time, and Date
The accuracy of your stargazing app hinges on correct location, time, and date settings. These settings are the foundation upon which the app calculates the positions of celestial objects.
- Location Settings: Most apps utilize your smartphone’s GPS to automatically detect your location. However, you can often manually enter your coordinates (latitude and longitude) if GPS isn’t available or if you want to simulate stargazing from a different location. This is useful for planning viewing sessions from specific locations, even if you’re not physically there.
- Time and Date Settings: Ensure your device’s time and date are accurate. Stargazing apps use this information to calculate the positions of stars, planets, and other objects. Some apps offer automatic time synchronization, while others allow manual input. Double-check for daylight saving time, which can affect the app’s calculations.
- Time Zones: Be mindful of time zones, especially when planning stargazing sessions across different regions. The app needs to know your current time zone to accurately display celestial object positions.
Using Time Travel Features
One of the most exciting features of stargazing apps is the ability to “time travel,” allowing you to see the sky at different times, past or future. This is incredibly useful for planning observations and understanding celestial movements.
- How Time Travel Works: The app recalculates the positions of celestial objects based on the date and time you select. You can typically move forward or backward in time using sliders, buttons, or direct input.
- Planning Observing Sessions: Use time travel to determine the best times to view specific objects. For example, you can find out when a planet rises or sets, or when a meteor shower will be at its peak.
- Understanding Celestial Motion: Time travel lets you visualize the movement of celestial objects across the sky. You can watch the Sun, Moon, and planets traverse the heavens, gaining a deeper understanding of their orbital paths.
- Example: Imagine you want to observe the Orion constellation. By using the time travel feature, you can find out when Orion is high in the sky at your location. This will give you the best chance of a clear view.
Filtering Objects by Criteria
Stargazing apps often provide powerful filtering options to help you focus on specific objects of interest. These filters allow you to narrow your search based on various criteria.
- Magnitude Filtering: This is a crucial filter. Magnitude represents the brightness of an object. A lower magnitude indicates a brighter object. You can filter objects based on their magnitude to see only the brightest stars and planets, or to focus on fainter deep-sky objects. For example, you could set a filter to only show objects brighter than magnitude 3.0.
- Object Type Filtering: Many apps allow you to filter by object type, such as planets, stars, constellations, galaxies, nebulae, and star clusters. This helps you concentrate on specific categories of celestial objects.
- Constellation Filtering: You can filter to view objects within a specific constellation. This is helpful when learning the constellations and identifying objects within them.
- Other Filtering Criteria: Some apps offer advanced filtering options, such as filtering by distance, apparent size, or object name. Experiment with these filters to discover what works best for your stargazing goals.
- Example: If you are looking for the Andromeda Galaxy, a magnitude filter can help you. Filter objects by magnitude and set the maximum magnitude to around 4.0 or 4.5. This should show you the galaxy, along with other objects of similar brightness.
Troubleshooting and Common Problems
Using stargazing apps is generally a smooth experience, but sometimes you might encounter issues. This section provides solutions for common problems you might face, ensuring you get the most out of your stargazing adventures. From inaccurate object identification to sensor glitches and the effects of light pollution, we’ll cover the troubleshooting steps to help you navigate these challenges.
Inaccurate Object Identification Solutions
Sometimes, the app might misidentify celestial objects. This can be frustrating, but there are several reasons and solutions.
- Calibration Issues: The app relies on your phone’s sensors (accelerometer, gyroscope, compass) to determine its orientation. If these sensors are not properly calibrated, the app will display incorrect information.
- Solution: Recalibrate your phone’s sensors. Most apps have a calibration option in their settings. You may need to move your phone in a figure-eight pattern or follow on-screen instructions.
- Obstructions: Trees, buildings, or other obstructions can block the app’s view of the sky. This can lead to incorrect object identification.
- Solution: Ensure you have a clear view of the sky. Move to a location with an unobstructed view, ideally away from trees, buildings, and other obstacles.
- Magnetic Interference: Electronic devices, metal objects, and even power lines can interfere with your phone’s compass, leading to inaccurate readings.
- Solution: Stay away from sources of magnetic interference. Keep your phone away from metal objects, other electronic devices, and power lines.
- Weak GPS Signal: A weak GPS signal can make it difficult for the app to pinpoint your location accurately, which can affect object identification.
- Solution: Ensure you have a strong GPS signal. Move to an open area with a clear view of the sky to improve GPS reception.
- App Bugs or Data Issues: Occasionally, the app itself might have bugs or data errors.
- Solution: Check for app updates. Ensure you have the latest version of the app installed. If the problem persists, try restarting the app or reinstalling it. You can also check the app’s support documentation or contact the developer for assistance.
Dealing with Light Pollution
Light pollution significantly impacts stargazing. Even with a stargazing app, the brightness from artificial lights can obscure faint celestial objects. Here’s how to mitigate its effects:
- Choose the Right Location: The location significantly impacts how well you can see the stars.
- Solution: Get away from urban areas. The farther you are from city lights, the better. National parks, remote areas, and dark-sky reserves are ideal. Consider using a light pollution map (available online) to find areas with minimal light pollution. For instance, a location 50 miles from a major city can offer significantly better viewing conditions than a location within the city limits.
- Use Filters: Certain filters can help.
- Solution: Use a light pollution filter (if your app has this feature). Some apps have a built-in light pollution filter that adjusts the display to compensate for the brightness. If you’re using a telescope, consider using a light pollution filter for the eyepiece. These filters selectively block certain wavelengths of light emitted by artificial sources.
- Observe During the New Moon: The phase of the moon can impact stargazing.
- Solution: Observe during the new moon. The moon’s brightness can also contribute to light pollution. Plan your stargazing sessions around the new moon when the moon is not visible in the night sky. This will maximize the visibility of fainter objects.
- Increase Exposure Time (if applicable): This applies to astrophotography.
- Solution: If you’re using your phone’s camera to capture images, increase the exposure time. This allows the camera to collect more light, making fainter objects visible. Note that this might require a tripod to keep your phone steady.
Troubleshooting Phone Sensor Issues
Your phone’s sensors are critical for stargazing app functionality. Here’s how to address sensor-related problems:
- Sensor Calibration: Regular calibration is essential for accurate readings.
- Solution: Recalibrate your phone’s sensors. Most stargazing apps provide a calibration option within their settings. Follow the app’s instructions, which usually involve moving your phone in a specific pattern (like a figure-eight) or rotating it in all directions. Recalibrate before each stargazing session.
- Sensor Interference: External factors can affect sensor accuracy.
- Solution: Minimize interference. Keep your phone away from metal objects, magnets, and other electronic devices that can interfere with the compass and other sensors. For instance, placing your phone on a metal table can cause significant compass errors.
- Software Updates: Keep your phone’s operating system updated.
- Solution: Ensure your phone’s operating system is up to date. Software updates often include sensor improvements and bug fixes that can enhance app performance. Check your phone’s settings for available updates.
- Restarting the App and Phone: Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve sensor issues.
- Solution: Restart the app and your phone. Closing and reopening the app can clear temporary glitches. Restarting your phone can reset the sensors and resolve more persistent issues.
- Hardware Problems: If the problem persists, there may be a hardware issue.
- Solution: Contact your phone manufacturer or a qualified repair technician. If none of the above solutions work, the issue might be with the phone’s hardware. In this case, you may need to seek professional assistance.
Maximizing Your Stargazing Experience
Now that you’ve mastered the basics of using stargazing apps, let’s explore how to elevate your stargazing sessions to create truly memorable experiences. This involves understanding the importance of dark skies, planning your outings effectively, and equipping yourself with the right accessories.
Importance of Dark Skies
Light pollution significantly impacts the visibility of celestial objects. The more light pollution present, the fewer stars and other objects you’ll be able to see. The best stargazing experiences happen under dark skies, away from city lights and artificial illumination.
Planning Stargazing Sessions
Successful stargazing requires careful planning. Consider these factors when planning your session:
- Best Times for Stargazing: The optimal time for stargazing is during the new moon phase, when the moon is not visible in the night sky. This minimizes the moon’s light, allowing fainter objects to be seen. Also, plan your sessions for clear nights, avoiding cloudy or hazy conditions. The best viewing times are generally a few hours after sunset and before sunrise, when the sky is darkest.
- Choosing Locations: The ideal location is far from city lights, streetlights, and other sources of artificial illumination. Rural areas, state parks, national parks, and remote wilderness areas are excellent choices. Check light pollution maps online (many apps provide this functionality) to identify areas with minimal light pollution.
- Weather Conditions: Always check the weather forecast before heading out. Clear skies are essential for stargazing. Look for forecasts that indicate low cloud cover and good visibility.
- Seasonal Considerations: The night sky changes throughout the year. Different constellations and celestial events are visible at different times. Research the constellations and events that will be visible during your planned session.
- Safety: Always prioritize safety. Let someone know your plans and expected return time. Bring a fully charged phone, a flashlight (preferably with a red light setting to preserve night vision), and appropriate clothing for the weather. Be aware of your surroundings and any potential hazards.
Essential Stargazing Accessories
Enhance your stargazing experience with the right accessories:
- Red-Light Flashlight: Preserves your night vision, allowing you to see the stars more clearly.
- Warm Clothing: Even on warm days, temperatures can drop significantly at night, especially in rural areas.
- Comfortable Seating: A reclining lawn chair or a blanket will make your stargazing experience more enjoyable.
- Binoculars: Enhance your view of the night sky, allowing you to see details not visible to the naked eye. Choose binoculars with a wide field of view and good light-gathering capabilities.
- Telescope (Optional): For a more detailed view of celestial objects, consider using a telescope. Start with a beginner-friendly telescope with simple controls.
- Star Charts or Guides: Provide a visual reference to help you identify constellations and other objects. Stargazing apps can also serve this purpose.
- Snacks and Drinks: Bring refreshments to keep you comfortable and energized throughout your stargazing session.
- Bug Spray: Protect yourself from mosquitoes and other insects, especially during warmer months.
- Notebook and Pen: For recording observations and sketching what you see.
Enhancing Your Knowledge of the Night Sky
Stargazing apps are fantastic tools for identifying celestial objects in real-time, but they are even more powerful when combined with a solid understanding of the night sky. The apps provide the ‘what,’ but a deeper knowledge base unlocks the ‘why’ and ‘how,’ transforming a casual observation into a richer, more meaningful experience. By supplementing your app usage with educational resources, you can truly unlock the wonders of the cosmos.
Resources for Learning About Celestial Objects
Learning about constellations, planets, and other celestial objects requires a multifaceted approach, combining visual aids, textual resources, and active observation. There are many avenues for learning, catering to different learning styles and preferences.
- Constellation Guides and Atlases: These resources provide detailed maps of the constellations, highlighting their stars and associated mythology. They often include information about the best times to view each constellation, their historical significance, and how to locate them in the night sky. A good atlas can also help you visualize the three-dimensional structure of the universe.
- Planetarium Software: Programs like Stellarium or similar, available on both computers and smartphones, allow you to simulate the night sky from any location and time. They are excellent for understanding the movement of planets, the phases of the moon, and the positions of constellations throughout the year. They offer a dynamic and interactive way to learn.
- Astronomy Websites and Blogs: Many websites and blogs are dedicated to astronomy, offering articles, news, and tutorials. These resources often provide up-to-date information on astronomical events, discoveries, and observing tips. Look for reputable sources like NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), and university astronomy departments.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Khan Academy offer a wide range of astronomy courses, from introductory to advanced levels. These courses provide structured learning experiences, often including video lectures, quizzes, and assignments. They’re a great way to build a strong foundation in astronomy.
- Observing Clubs and Societies: Joining a local astronomy club or society provides opportunities to learn from experienced observers, share your knowledge, and participate in group observing sessions. These clubs often host lectures, workshops, and star parties, providing a supportive and engaging environment for learning.
Connection Between Stargazing Apps and Astronomy Education
Stargazing apps serve as a bridge between technology and astronomy education. They can be used to supplement formal and informal learning experiences, making the subject more accessible and engaging.
- Real-time Identification: Apps instantly identify celestial objects, allowing users to confirm what they are seeing in the sky. This immediate feedback reinforces learning and builds confidence.
- Interactive Learning: Apps often include information about celestial objects, such as their distance, size, and history. This information is presented in an interactive and accessible format, making it easier to understand complex concepts.
- Visualizations and Simulations: Many apps provide visualizations of celestial events, such as eclipses and meteor showers. These simulations can help users understand these events and their impact on the night sky.
- Accessibility: Stargazing apps make astronomy more accessible to people of all ages and backgrounds. They eliminate the need for expensive equipment and complex calculations, making it easier to explore the universe.
- Personalized Learning: Apps can be tailored to individual learning preferences and skill levels. Users can choose to focus on specific objects or constellations, or they can explore the entire night sky.
Recommended Astronomy Books and Websites
Selecting the right resources is crucial for effective learning. Here’s a list of recommended astronomy books and websites, catering to different interests and skill levels.
- Books:
- NightWatch: A Practical Guide to Viewing the Universe by Terence Dickinson and Alan Dyer: A comprehensive guide for beginners, covering everything from telescopes to observing techniques.
- Turn Left at Orion: Hundreds of Night Sky Objects to See in a Small Telescope–and How to Find Them by Guy Consolmagno and Dan M. Davis: A practical guide to observing specific objects with a small telescope.
- The Sky Atlas 2000.0 by Wil Tirion: A detailed atlas of the night sky, ideal for serious observers.
- Websites:
- NASA (nasa.gov): The official website of NASA, providing information on space exploration, discoveries, and educational resources.
- ESA (esa.int): The official website of the European Space Agency, offering information on European space missions and research.
- Sky & Telescope (skyandtelescope.org): A leading astronomy magazine’s website, with articles, observing guides, and news.
- Astronomy Magazine (astronomy.com): Another popular astronomy magazine’s website, providing articles, images, and videos.
- Heavens-Above (heavens-above.com): A website that predicts the times when satellites, including the International Space Station, will be visible from your location.
Future of Stargazing Apps
The world of stargazing apps is constantly evolving, fueled by advancements in technology and a growing interest in astronomy. These apps are poised to become even more sophisticated and user-friendly, offering a richer and more immersive experience for both casual observers and seasoned enthusiasts. Let’s delve into the emerging trends and potential future features that will shape the landscape of stargazing apps.
Emerging Trends in Stargazing App Technology
Several key trends are driving innovation in stargazing apps. These advancements are not just about adding new features; they’re about enhancing the overall user experience and making astronomy more accessible to everyone.
- Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: AR is becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing apps to overlay digital information onto the real-world view through a smartphone’s camera. This means users can point their phones at the sky and see constellations, planets, and other celestial objects superimposed directly onto the live view. Expect even more seamless and accurate AR experiences in the future, with improved object recognition and dynamic adjustments based on the user’s location and time.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML are being used to analyze vast amounts of astronomical data, personalize the user experience, and automate complex tasks. This can include features like personalized recommendations for viewing objects, automated object tracking, and even the ability to identify celestial objects based on user-provided data (e.g., a blurry image captured through a telescope).
- Integration with Smart Telescopes: The convergence of stargazing apps and smart telescopes is another significant trend. Many modern telescopes can be controlled directly from a smartphone or tablet via an app. This integration allows users to easily find and track celestial objects, and even capture images and videos directly from the telescope, streamlining the entire stargazing process.
- Advanced Data Visualization: The way data is presented to users is constantly evolving. Expect to see more interactive 3D models of the solar system, more detailed representations of nebulae and galaxies, and the incorporation of data from space-based observatories like the James Webb Space Telescope. This enhanced visualization will provide a deeper understanding of the cosmos.
Potential Future Features and Functionalities
The future of stargazing apps holds exciting possibilities, with new features designed to enhance the user experience and provide even more in-depth astronomical knowledge.
- Personalized Learning Paths: Apps could offer customized learning paths based on a user’s skill level and interests. This might involve quizzes, interactive tutorials, and curated content to guide users through the basics of astronomy and beyond.
- Social Features and Community Building: Stargazing apps could incorporate social features that allow users to connect with each other, share their observations, and participate in virtual stargazing events. This could foster a sense of community and encourage collaboration among astronomy enthusiasts.
- Advanced Image Processing and Analysis: Integration of sophisticated image processing tools could allow users to enhance and analyze images captured through telescopes or smartphones. This might include features like stacking multiple images to reduce noise, applying filters to reveal hidden details, and identifying specific features in astronomical images.
- Real-Time Data Feeds: Access to real-time data from observatories and space agencies could provide users with up-to-the-minute information about celestial events, such as meteor showers, solar flares, and the positions of satellites.
- Integration with Wearable Devices: Stargazing apps could be integrated with wearable devices, such as smartwatches, to provide hands-free information and alerts during stargazing sessions. This could include notifications about upcoming celestial events, directions to find specific objects, and even haptic feedback to guide the user’s gaze.
How Stargazing Apps Will Continue to Evolve
The evolution of stargazing apps will be driven by a combination of technological advancements, user feedback, and the ever-expanding knowledge of the universe. Here’s how these apps are likely to develop:
- Greater Accessibility: Apps will become even more user-friendly and accessible to people of all ages and backgrounds. This will involve intuitive interfaces, simplified explanations, and support for multiple languages.
- Enhanced Accuracy and Reliability: The accuracy of object identification and tracking will continue to improve, thanks to advancements in GPS technology, sensor data, and astronomical databases.
- Increased Integration with Other Technologies: Stargazing apps will seamlessly integrate with other technologies, such as smart home devices, virtual reality (VR) headsets, and augmented reality (AR) glasses, to provide a more immersive and interactive experience.
- More Data and Information: Apps will provide access to even more astronomical data, including detailed information about celestial objects, their properties, and their place in the universe. This data will be sourced from both professional observatories and citizen science projects.
- Focus on Education and Outreach: Stargazing apps will play an increasingly important role in promoting science education and public outreach. They will be used in classrooms, museums, and science centers to engage students and the public with the wonders of the cosmos.
Outcome Summary

In conclusion, mastering How to Use Stargazing Apps on Your Smartphone opens up a universe of possibilities. You’ve learned how to select the right app, navigate its interface, and identify celestial objects. With the right tools and a little practice, you’re now ready to explore the cosmos from the comfort of your own backyard. So, grab your phone, step outside, and prepare to be amazed by the beauty and mystery of the night sky.
The universe awaits!